BY McCormick Center | May 26, 2016

Sim Loh is a family partnership coordinator at Children’s Village, a nationally-accredited Keystone 4 STARS early learning and school-age enrichment program in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, serving about 350 children. She supports children and families, including non-English speaking families of immigrant status, by ensuring equitable access to education, health, employment, and legal information and resources on a day-to-day basis. She is a member of the Children First Racial Equity Early Childhood Education Provider Council, a community member representative of Philadelphia School District Multilingual Advisory Council, and a board member of Historic Philadelphia.
Sim explains, “I ensure families know their rights and educate them on ways to speak up for themselves and request for interpretation/translation services. I share families’ stories and experiences with legislators and decision-makers so that their needs are understood. Attending Leadership Connections will help me strengthen and grow my skills in all domains by interacting with and hearing from experienced leaders in different positions. With newly acquired skills, I seek to learn about the systems level while paying close attention to the accessibility and barriers of different systems and resources and their impacts on young children and their families.”
This document may be printed, photocopied, and disseminated freely with attribution. All content is the property of the McCormick Center for Early Childhood Leadership.
This resource is part of our Research Notes series.
Administrators’ qualifications often differ across sectors of the early childhood field—school-based pre-K programs, center-based child care, and Head Start. School principals overseeing school-based programs typically have a minimum of a master’s degree in educational leadership with administrative certification. Child care center directors’ qualifications vary widely from minimal requirements for licensure to extensive specialized education and experience. Currently, Head Start Performance Standards do not specify minimum qualifications for site-level managers, but changes to these requirements are being considered as the regulations for this federal program are revised.
Minimum qualifications in education, experience, and specialized training are needed in all sectors of the field to ensure that individuals leading and managing early childhood programs are adequately prepared. This Research Note provides a focused look at Head Start and Early Head Start administrators.
The McCormick Center examined workforce data regarding Head Start and Early Head Start education coordinators and site-level managers in Illinois to learn more about their qualifications. For clarity, two levels of administration were considered—grantee level and site level. Separate data sources for each level were analyzed to identify administrative qualifications.
SAMPLE AND DATA SOURCES
Education Coordinators at the Grantee Level. The Office of Head Start provides access to comprehensive data on the services and staff serving in Head Start and Early Head Start programs collected from the mandatory Program Information Report (PIR).1 National and Illinois agency information was examined for the 2014-2015 program year. Illinois has 47 Head Start grantees with 137 programs.2 Table 1 shows the number and percentage of programs.
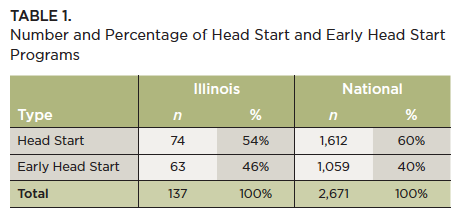
Of these programs, there were 258 individuals reported as education coordinators3 in Illinois and 6,714 individuals across the United States. Data about the qualifications of other administrators (executive directors, site-level managers, program directors, etc.) were not available through the PIR.
Site-Level Managers. The Gateways to Opportunity Registry4 collects data about the early childhood workforce in Illinois and provided site-level data on 593 Head Start and Early Head Start individuals who self-identified as administrators.5 Individuals from three Gateways job position categories were analyzed:
- Director/Administrator (one site)
- Director/Administrator (multi-site)
- Director/Teacher
Gateways also verifies administrators’ qualifications for the Illinois Director Credential6 issued by the Illinois Department of Human Services. Of those that self-identified as Director/Administrators or Director/Teachers, there were 130 Head Start or Early Head Start administrators who had earned an Illinois Director Credential (IDC).
RESULTS
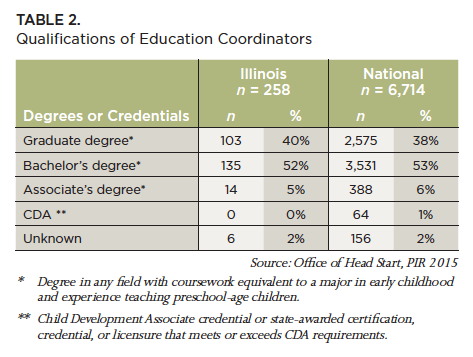
Education Coordinators at the Grantee Level. Both in Illinois and nationally, over 90% of education coordinators have a bachelor’s degree or higher in early childhood with teaching experience. However, 7% in Illinois do not meet the mandatory qualification requirements for Head Start education coordinators.7 Table 2 shows the qualifications of Education Coordinators by degree categories.
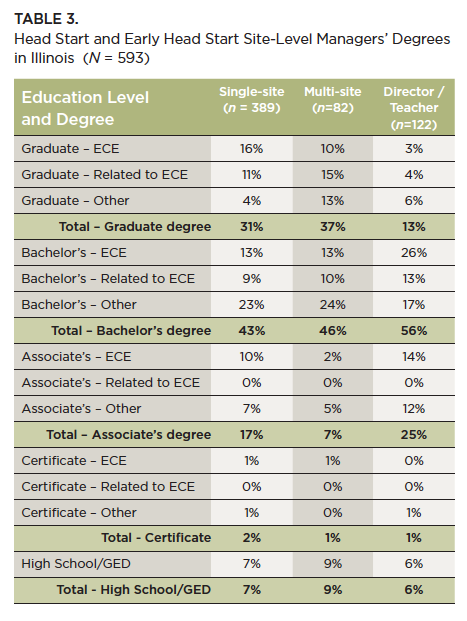
Site-Level Managers. Of the 593 site-level managers in the sample, 74% reported having earned a bachelor’s degree or higher; 28% with graduate degrees and 46% with bachelor’s degrees. About one-fourth of administrators serving as site managers (of both single-site and multi-site programs) earned a graduate degree. Directors/Administrators of multiple sites had the highest levels of education with 82% having a bachelor’s degree or higher. Table 3 shows the percentages of Head Start site-level managers’ degrees attained in the three job position categories and whether the individuals majored in early childhood education, a related discipline, or another field of study (including those that did not report a major).8
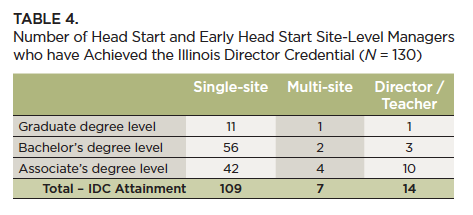
Illinois Director Credential Attainment. The status of Head Start and Early Head Start site-level managers’ credential attainment was examined by role. There are approximately 14 Head Start and Early Head Start site-level managers with an Illinois Director Credential (IDC) at the graduate level and 71 individuals with an IDC at the bachelor’s level.9 This represents about 15% of the Head Start site-level managers in the state. Qualifications to meet the criteria for these credentials are verified in the Gateways system and include formal education, specialized training in leadership and management, and management experience. Table 4 shows the number of IDC credentials attained by Head Start site-level managers in the three job position categories.
IMPLICATIONS FOR POLICY, PRACTICE, AND RESEARCH
These findings affirm that most Head Start and Early Head Start administrators in Illinois have formal coursework and expertise in child development and early childhood education. In Illinois, 40% of education coordinators at the grantee level have graduate degrees in or related to early childhood and nearly one-fourth of administrators at the site-level earned graduate degrees related to early childhood. However, these findings reveal that one-fourth of the site-level managers in Illinois fail to meet the federal education mandates for classroom teachers—a bachelor’s degree. The Office of Head Start should ensure that minimum qualifications for administrators at all levels meets or exceeds those of classroom teachers in their programs and include specialized formal education that includes both pedagogical leadership and administrative leadership.
At the McCormick Center, we believe that in learning organizations, such as Head Start centers, whole leadership is needed to address the multifaceted demands of the organization. Administrators must demonstrate balanced skills that include leadership to meet the organizational needs and leadership to improve and support teaching and learning. A key role of site level administrators in learning organizations is to provide pedagogical leadership. Even if the program affords an education coordinator—a content area expert—to support teaching and learning, the site-level manager also influences classroom practice. A pedagogical leader must be aware of the learning styles of individual teachers and the collective group to establish a norm of continuous quality improvement. Effective pedagogical leaders must be competent in discerning the needs of children and guiding the curricular program to optimize learning.
Head Start administrators on multiple levels also need to possess knowledge and skills regarding administrative leadership. Especially at the site level, managers must have the ability to implement effective systems and lead individuals for sustained programmatic success. The Illinois Director Credential is a good indicator that administrators are competent in both pedagogical and administrative leadership. The small percentage of credentialed administrators leading Head Start and Early Head Start programs in Illinois raises questions about their overall balanced capabilities. From a policy perspective, targeted efforts should be made to support Head Start and Early Head Start site level administrators (managers and education coordinators) to pursue attainment of the Illinois Director Credential.
The McCormick Center is grateful for assistance provided by Gateways to Opportunity: Illinois Professional Development System, the Illinois Head Start State Collaboration Office, and the Illinois Head Start Association for providing data and their support in preparing this brief.
ENDNOTES
- U. S. Department of Health and Human Services, Office of Head Start, Early Childhood Learning and Knowledge Center (ECLKC), Program Information Report (PIR): https://hses.ohs.acf.hhs.gov/pir/
- A grantee may have multiple programs (e.g., Head Start and Early Head Start) and/or separate programs provided by delegate agencies.
- Education Coordinators (or Managers) provide content expertise in key areas including child growth and development, early childhood education, and family support. The titles of these staff members vary but their role usually includes coaching teachers in the implementation of curricula. These individuals may provide leadership at multiple sites or assume responsibility for oversight and supervision of classrooms at a single location.
- Gateways to Opportunity Registry 2015 Dataset (INCCRRA)
- The site’s DCFS license number was used as the unique identifier to match data between sites receiving Head Start/Early Head Start funding and individuals working at those sites. Administrators working at license-exempt sites are not represented.
- Gateways Credentials Overview: http://www.ilgateways. com/en/credentials
- “Qualifications of content area experts…Education and child development services must be supported by staff or consultants with training and experience in areas that include: The theories and principles of child growth and development, early childhood education, and family support. In addition, staff or consultants must meet the qualifications for classroom teachers, as specified in section 648A of the Head Start Act and any subsequent amendments regarding the qualifications of teachers.” (45 CFR 1304.52 d 1)
- Majors are defined as: ECE – early childhood education, child development, family and consumer sciences; Related – elementary education, social work, curriculum and instruction; and Other – no major reported or not in ECE or related field.
- Graduate, bachelor’s, and associate’s levels correspond with Levels I, II, and III for the IDC respectively.





