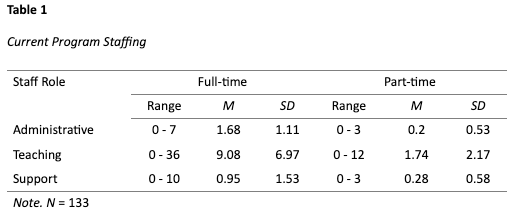
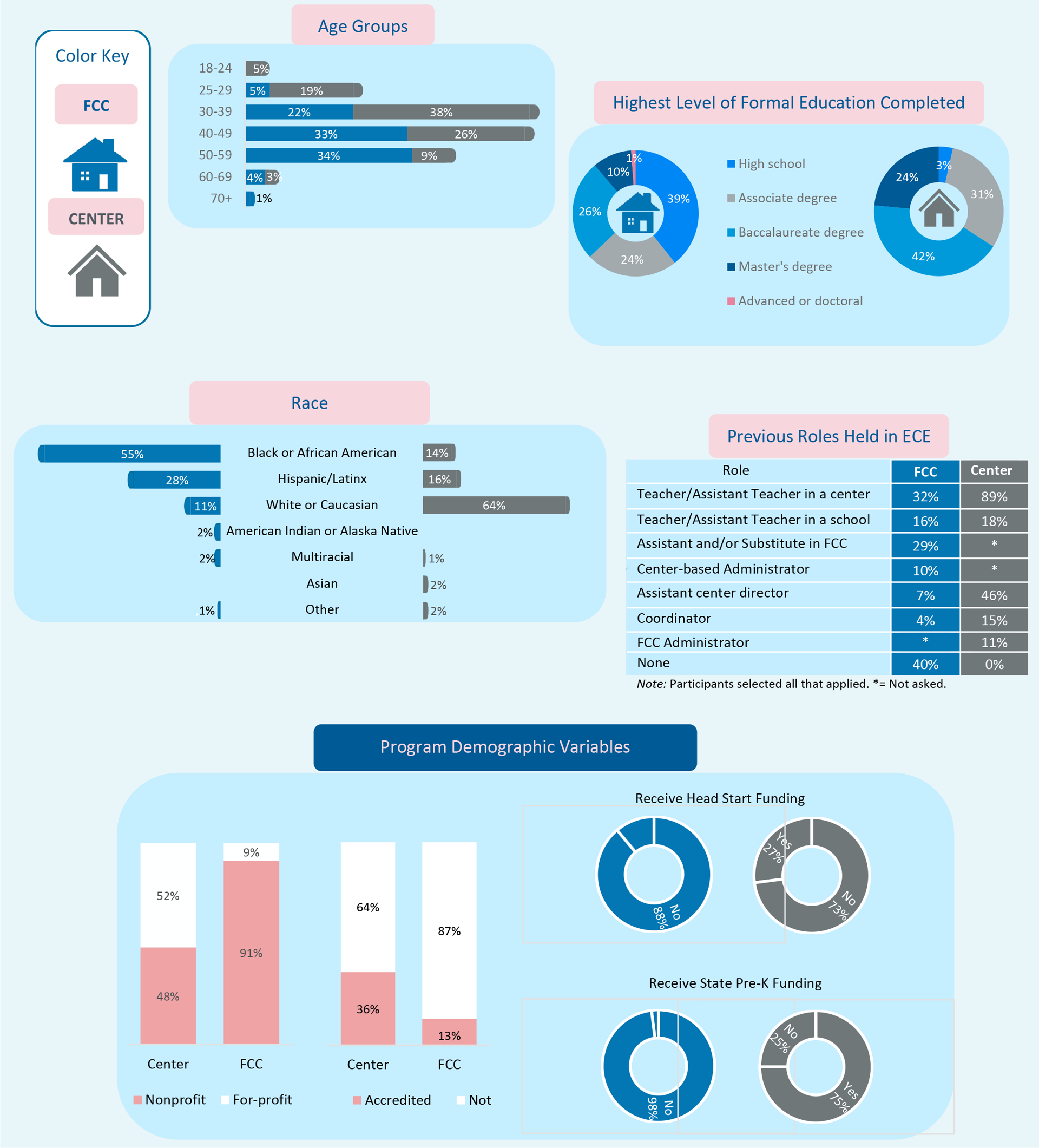
These resources include detailed and thought-provoking studies on important topics, concise summaries of research relating to early childhood professional development and workforce issues (Research Notes), and important documents explaining requirements to become director-qualified. Our research aims to inform policy to embed quality supports for early childhood leadership in state and federal initiatives.
Latest Resources - Research
October 23, 2024
Maintain your BAS Assessor status with recertification required two years after initial certification. Learn about eligibility, steps, and deadlines.
By McCormick Center
•
May 13, 2025
Learn how assessing organizational conditions can drive continuous quality improvement in early childhood programs.
By Teri Talan
•
August 9, 2022
This document may be printed, photocopied, and disseminated freely with attribution. All content is the property of the McCormick Center for Early Childhood Leadership.
By Teri Talan, J.D., Ed.D.
•
October 4, 2021
This document may be printed, photocopied, and disseminated freely with attribution. All content is the property of the McCormick Center for Early Childhood Leadership.