BY Dr. Teri Talan, Senior Policy Advisor | April 15, 2020
This document may be printed, photocopied, and disseminated freely with attribution. All content is the property of the McCormick Center for Early Childhood Leadership.
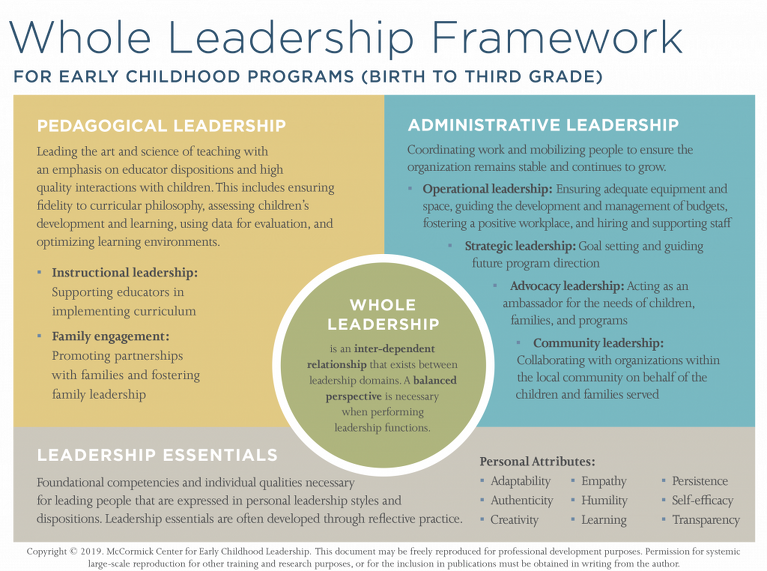
Leadership Essentials Modules
Module 1: Leading the Way
This module assists a program leader in understanding the vital role played in creating and sustaining program excellence.
- Identify and describe the skills and competencies required for effective leadership
- Examine the values and beliefs that shape leadership behavior while also determining a compelling program vision and mission statement
- Interpret one’s unique leadership style
- Identify and apply ways to use your influence to empower others
- Recognize ethical dilemmas related to leading others
- Examine and apply one’s own leadership essentials within the framework of Whole Leadership
Module 3: Promoting Peak Performance
This module assists a program leader to understand the central role they play in supervising staff and building a learning community by guiding teachers to become reflective practitioners.
- Recognize and apply the concepts of motivation theory
- Apply a developmental approach to supervision which includes the use of coaching/mentoring and individualized professional development plans
- Use performance appraisals based on observation of practice to support reflective practice
- Promote a positive work environment based on embedded norms of communication, collaboration, and shared leadership
- Identify strategies for managing conflict and difficult people
- Describe the importance of a professional learning community to high-performing teams
Module 9: Evaluating Program Quality for Continuous Improvement
This module focuses on the critical role that a program leader provides by modelling for staff and demonstrating to facilities, a program’s commitment to ongoing inquiry and quality improvement.
- Describe the purpose, types, and ethics of program evaluation
- Select appropriate program evaluation tools
- Utilize evaluation tools to assess program needs and to support continuous quality improvement (CQI)
- Identify desired outcomes for program improvement
- Plan strategically for program improvement through repeated cycles of inquiry
- Build norms of continuous quality improvement (CQI) by engaging families and staff in collaborative program evaluation
Administrative Leadership Modules
Module 2: Recruiting, Selecting, and Orienting Staff
This module increases a program leader’s understanding of and ability to implement effective, ethical, and lawful employment practices.
- Recognize issues related to employee recruitment in the field of early care and education
- Develop and implement a model of continuous recruitment
- Review strategies to empower staff by involving them in the hiring process
- Examine strategies when screening, interviewing, and selecting candidates
- Apply fit criteria when selecting the best applicant
- Design and recommend a phased orientation of new employees
Module 4: Managing Program Operations
This module expands a program leader’s understanding of systems thinking to evaluate and implement efficient, strategic, and important management systems to alleviate risk within the early childhood program setting.
- Examine the complexity of operational management and leadership including the application of systems theory to support necessary operating systems
- Identify stakeholders and practice a strategic planning process
- Investigate quality benchmarks related to program operations within the subscales of the Program Administration Scale (PAS)
- Use specific tools for managing systems including standard operating procedures, workflow analysis, calendars, and Gantt charts
- Explore additional health and safety policies and procedures to protect the early childhood program, the children, families and program staff
- Identify core elements of a disaster preparedness and emergency evacuation plan
- Review preventative best practices in risk management to avoid potential allegations of child abuse and neglect
Module 5: Building a Sound Business Strategy
This module introduces the program leader with the decisions regarding the program’s organizational structure, its finances, and the way of caring for existing and prospective customers.
- Identify core values related to business orientation
- Examine legal forms of business ownership common to early childhood programs
- Investigate the quality benchmarks associated with budget planning as identified in the Program Administration Scale (PAS)
- Calculate a budget and cash flow projection to plan program finances.
- Review best practice use of program management software utilized to support office operations and enhance digital communication
- Identify approaches to grant writing, including responding to funding opportunities to blend or braid funds to support quality programming
- Apply best practices when implementing public relations and marketing strategies to enhance external customer relationships and program operations
Pedagogical Leadership Modules
Module 6: Designing Indoor and Outdoor Environments
This module will strengthen your program and leadership capacity as you plan, evaluate, and improve indoor and outdoor environments for infants, toddlers, pre-K, and school-age children to create the highest quality setting for children, families, and staff to thrive.
- Explain the impact of the physical setting on behavior and learning
- Plan for specific developmental, caregiving, and learning needs in infant, toddler, preschool, and after-school program settings
- Describe the design elements of settings and materials with implications for planning, supervision, access, and accountability
- Provide feedback to strengthen teacher competencies in preparing child-centered play, learning, and activity spaces
- Locate resources and materials to ensure alignment of your setting with quality rating improvement systems, licensing, and regulatory requirements
Module 7: Supporting Children’s Development and Learning
This module will build your program capacity to advance children’s development and learning by providing leadership to establish and strengthen staff competencies for teaching and caregiving.
- Explain pedagogical leadership and its impact on your program’s mission and goals
- Identify elements of high-quality early childhood teaching
- Describe integration of child development with learning
- Evaluate elements of observation, documentation, screening, and assessment.
- Implement social-emotional learning
- Provide oversight, feedback, and training for teachers to help them achieve required competencies of the profession
Module 8: Facilitating Responsive Family Engagement
This module will increase your leadership influence, activate strategies to promote family engagement, strengthen connections between family, program, and community resources.
- Identify the competencies and benefits of family engagement
- Describe and implement linguistically and culturally responsive practice
- Promote families’ role in relationship-based care and teaching
- Evaluate strategies for collaboration that promote child development
- Explain and implement trauma-informed program practices
- Examine and apply effective skills for communication and collaboration





